Outdoors "4 minutes" gold life-saving time
The sudden death caused by personal physical causes in outdoor sports is called outdoor sudden death. It mainly refers to sudden cardiac death, which means that it is a potential cause of death from cardiac death caused by fatal arrhythmias induced by excessive exercise. According to sports medicine, it not only refers to the sudden death that occurred during the donkey trip, but also included the discomfort that occurred during the donkey trip and the sudden death that occurred within one day after the end of the donkey trip. In other words: people and people are not the same, extreme, Asian extreme sports, for some friends at any time may be fatal.
Outdoor casualty law does not compensate?
On the outside, if there is sudden death in sports, the main responsibility should also be on the person concerned. If you already have a problem with your own heart, even if you go into outdoor insurance , the insurance company will still be exempt. Before reading an insurance case, the insurer's argument was: “He was not accidentally dead. Knowing that he had a heart attack and still participating in such a sport and that death was not an accident, was not expected. In a similar case, only the students who were under guardianship also suffered sudden death from physical activity during school-organized activities and it was decided that the school was responsible. And we adults in the usual AA restrictions associated with the activities, no one will be responsible for outdoor death, even if it is a commercial activity.
What should happen if a sudden death occurs around me?
It can be difficult to prevent death. It can happen at any time and place and it can happen to anyone. In a dying patient, the heartbeat stopped for more than 4-6 minutes and the brain tissue suffered permanent damage. More than 10 minutes will brain death! The ambulance cannot reach the patient within a few minutes. Therefore, it is still very necessary to learn a little first-aid knowledge. The key moments may save the family or others.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
First aid refers to emergency measures that are taken when the patient is breathing, the heart is stopped, or when breathing or heartbeat will stop. Because the supply of oxygen to the body can cause the patient to die in a matter of minutes, when a sudden change in the patient’s condition is detected, a “cpruccal resuscitation†that improves breathing and circulation must be performed in time. Sometimes even if the patient's breathing and circulation are restored by CPR, because brain cells lack oxygen for more than 4 to 5 minutes, the recovery of body functions will be difficult, resulting in severe sequelae. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is divided into unassisted pre-hospital care and in-hospital first aid using medical devices or drugs.
CPR steps:
1 Awareness level judgment 2 Open airway (A: Airway)
3 Breathing Breathing (B: Breathing)
4 cycles and C:Circulation.
1 consciousness level judgment
The patient's level of consciousness is judged by loud stimuli. Pat the patient's reaction by tapping the patient's shoulder and giving a loud call or slap on the patient's cheek to give painful stimulation.
2 open airways
Patients with low levels of consciousness are prone to airway obstruction due to falling back of the tongue or vomit, and deposition of food debris. To ensure smooth oxygen supply, it is important to ensure airway patency through the use of hands or using instruments.
Methods for opening the airway include airway foreign body removal method, open hand airway method, tracheal intubation method, and tracheostomy tube insertion method. Intra-airway foreign body removal method: used for foreign body blocking airway.
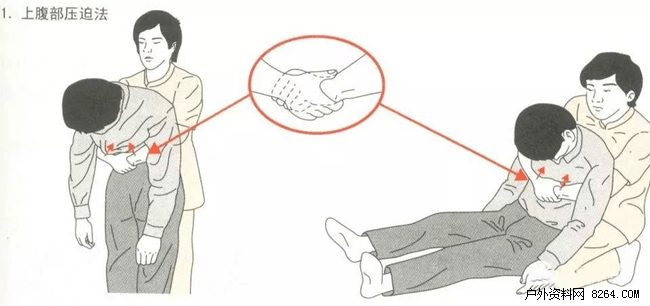
Upper abdominal compression
★ Operation steps
1 The operator holds the patient who takes the seat or seat from behind (Figure 1).
2 The operator's left hand fist hits the patient's abdomen, and the right hand holds the left hand.
3 The operator tightens both hands to the chest to press the abdomen of the patient so that the patient can push out the foreign body.
4 It can be repeated if it fails to get out of the foreign body once.
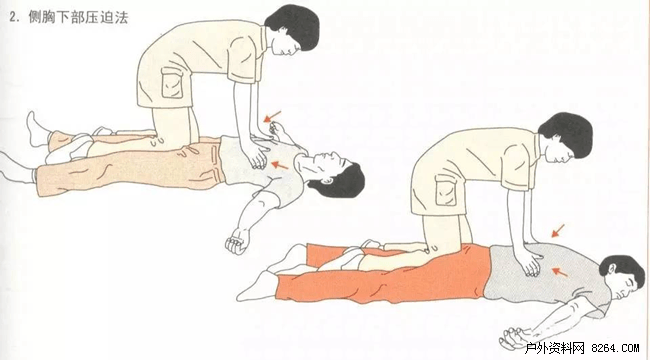
★ Operation steps
1 The patient was supine or prone, and the operator had both knees.
2 The operator opens his hands and puts them on both sides of the patient's thoracic cage and presses forcefully inwards and downwards, causing the patient to push out the foreign body (Figure 2).
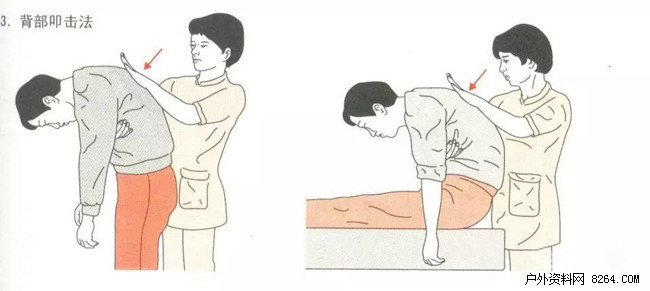
★ Operation steps
1 The patient takes the standing position or sitting position. The operator supports the patient's front chest wall with one hand, and the head of the patient is curved to the front chest (Figure 3).
2 The other hand of the operator strongly attacks the patient's scapula and causes the patient to cough up the foreign body.
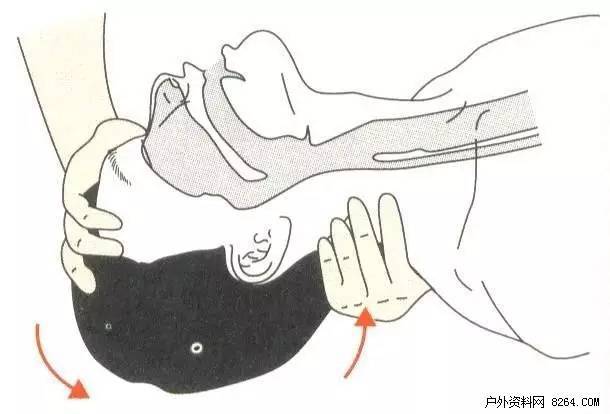
This is the easiest way to operate without any equipment. Including the head back method, head up jaw method, mandibular lift method, the best effect is the mandible lift method. Regardless of the method used, care should be taken to ensure that the patient is placed in a lateral position as far as possible. When there is a foreign body in the oral cavity, it can be quickly swaged with a gauze or other finger around the fingertip. When there is liquid foreign body in the mouth, it is easy to discharge if the patient is in a lateral position. When the patient has a spinal cord injury, head reflex and mandibular top lifting should not be used.
Head reflex
★ Operation steps
1 The operator is on one side of the patient's head.
2 Hold the patient's neck with one hand, place the other hand on the patient's forehead and extend the head backwards (Figure 4). Be careful not to overstretch injuries.
★ Operation steps
1 The operator is on one side of the patient's head.
2 The operator's hand is placed on the patient's forehead and the head is raised backwards.
3 The index finger and middle finger of the other hand are placed against the center of the mandible of the patient to close and lift the mouth (Figure 5).
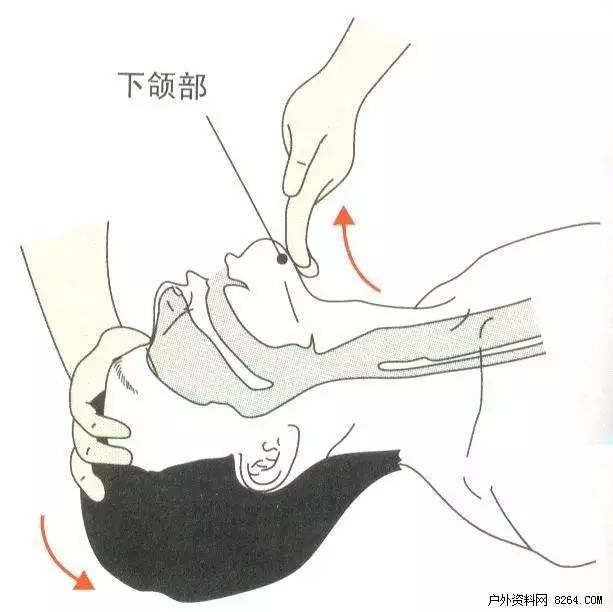
★ Operation steps
1 The operator is above the patient's head.
2 Use both hands to support the two sides of the mandibular angle, and lift the mandible with force so that the teeth below are the same as those listed above.
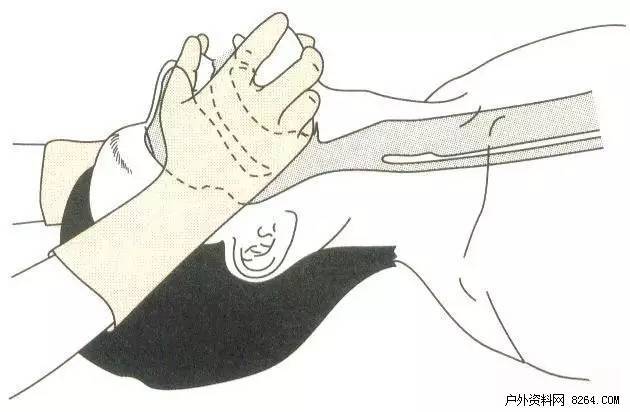
If you cannot resume spontaneous breathing or have weak spontaneous breathing after opening the airway, artificial respiration should be performed quickly. Observing whether there is spontaneous breathing or not by observing whether the activity of the thorax is restored or not, and whether or not there is breath sound near the patient's mouth and nose, or whether there is air flow generated by the patient's breathing with the cheek, etc.
Mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration
★ Operation steps
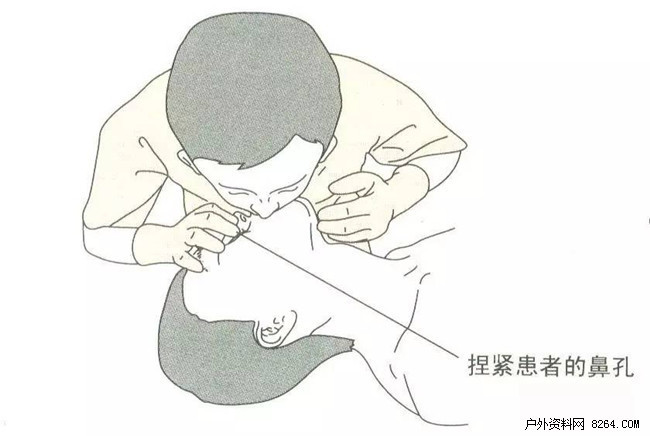
1 Open the airway with your head and flexing your arms and arms, and pinch the patient's nostrils.
2 The operator inhales air through the mouth and wraps the patient's mouth with his or her mouth or mask, slowly blowing air into the patient's airway and blowing it twice (Figure 7).
Observe the patient's chest. If there is no chest undulation indicating that air insufflation is ineffective, check for leaks from the patient's mouth or nose. If the abdomen bulges, it shows that the airway is not open enough, or the air blowing rate is too fast and excessive.
3 After 2 insufflations, the operator placed the ear on the patient's mouth and observed the ups and downs of the chest. If the insufflation was successful, the patient would exhale gas on his own and the abdomen would naturally recoil.
4 Repeatedly performed 2 to 3 procedures.
When the airway is opened and the heartbeat cannot be resumed after artificial respiration, the heartbeat can be determined to be stopped. Ventricular compression should be performed at the same time as artificial respiration. The method of confirming whether or not there is a heartbeat can be performed by touching the beat of the carotid artery or the ear close to the patient's heart.
Extracardiac compression - compression of the sternum external to the heart
★ Operation steps
1 The patient takes a supine position, and the back requires a hardwood to increase the pressure on the sternum when pressed.
2 Unfasten the patient's top, open the chest, the operator is located on one side of the patient.
3 Determine the location of the compression, the lower 1/3 of the sternum or the sternal body of the xiphoid 2 (Figure 8).

4 The operator places the palm root of one hand on the pressing area and the other hand on the front one. Do not touch the patient's chest with the fingers of both hands so as not to damage the ribs.
5 The shoulders, elbows and hands of the operator should be perpendicular to the patient's chest, and the two elbows should extend straight. The weight of the upper body should be used to exert pressure on the sternum (Figure 9).
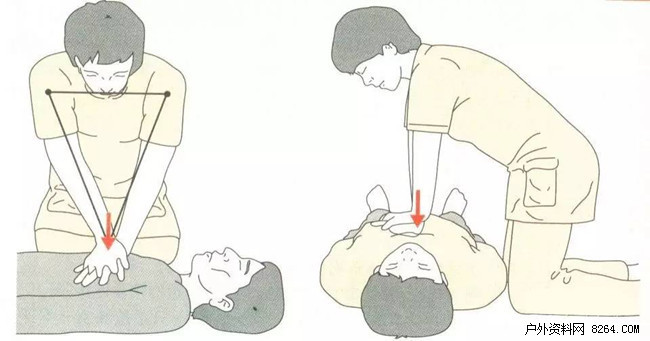
6 The depth of the press is preferably 3 to 5 cm in the sternum.
7 The position of the hand after one press is the same and the upper arm is relaxed. This is repeated 15 times after blowing 2 times. The ratio of out-of-heart massage to artificial respiration is 30:2 for single or double operation.
The first 4 minutes after a sudden death is the prime time for a rescue! The sooner the rescue begins, the higher the success rate and the fewer sequelae and complications. For each minute of delay, the rescue success rate drops by 10%.
Diameter of caster : 100MM
Width of caster : 32MM
Bearer : 90-136KG
Bearing : Ball Bearing and Axle tube
Height of caster : 130MM
Turning radius :81MM
Full Brake Turning radius : 127MM
Commonly used nylon fibers can be divided into two categories.
A class of polydydramines, which are made up of diamine and diacid, has a chemical structure of long-chain molecules:
H-[HN(CH2)xNHCO(CH2)yCO]-OH
The relative molecular weight of these nylons is generally 17,000-23,000. Depending on the number of carbon atoms used for binary amines and binary acids, different nylon products can be obtained and can be distinguished by the number added to the nylon, wherein the previous number is the number of carbon atoms of binary amines and the latter number is the number of carbon atoms of binary acids. For example, nylon 66 indicates that it is made of hexaamine and hexachloric acid, and nylon 610 indicates that it is made of hexamine and hexadic acid.
The other is derived from the concentration or open-loop polymerization of endamide, and the chemical structure of its long-chain molecules is:
H-[NH(CH2)xCO]-OH
According to the number of carbon atoms contained in its cell structure, different varieties can be named. For example, nylon 6, which means that it is made up of hexylamide open-loop polymerization containing six carbon atoms.

Braked Castors,Mid Duty Nylon Caster,Wheel Castors With Brakes,4 Inch Swivel Casters With Brake
GuangZhou XingGuang Caster Product Co LTD , https://www.cnxingguangcaster.com