AZ-S0101 Soil carbon and nitrogen conversion rate measurement system
introduction
In recent years, due to human activities, the nitrogen content in the ecosystem has been increasing.
The direct or indirect effects of fixation and plant nitrogen utilization have greatly intervened in the process of ecosystem carbon storage and nitrogen redistribution. Soil carbon and nitrogen conversion is a very important process of the carbon-nitrogen coupling cycle, which has important significance for the structure and function of terrestrial ecosystems. Soil respiration, nitrification and denitrification are important links in the carbon and nitrogen cycle. While promoting primary productivity, it may also cause soil acidification, nitrate leaching and N2O release, which is a potential cause of soil nitrogen loss and atmospheric environmental pollution. way. The quantitative study of soil carbon and nitrogen conversion rate has attracted more and more attention.
Among the methods that can simultaneously measure the rate of nitrification and denitrification, the 15N isotope method is the most direct, but this method requires adding
15N NO3- affects the authenticity of the culture samples, and the measurement is time-consuming and expensive; the acetylene suppression method is more traditional, mainly using acetylene to suppress the reduction of N2O to N2, and the denitrification loss is calculated by measuring the release of N2O, but later The study found that in the presence of oxygen and high concentration of acetylene, NO can combine with O2 to become NO2, and then to nitrite and nitrate, and this step cannot be accurately measured, resulting in deviations in results, so this method Was abandoned.
2 Measurement system design
2.1 Objective
AZ-S0101 soil carbon and nitrogen conversion rate measurement system, using the newly developed barometric process separation technology (Barometric Process Separation), taking the field undisturbed soil column as the object, mainly used to determine the conversion rate of carbon and nitrogen in soil microorganisms , Including total nitrification rate, denitrification rate and soil respiration rate, in well-ventilated soil, its accuracy is equivalent to 15N isotope tracing method. The system not only avoids the destruction of the original soil structure, but also does not need to add inhibitors or exogenous isotopes, effectively avoiding the soil pollution caused by the isotope tracing method and the original soil gas composition caused by the acetylene suppression method, etc. Change and other issues.
Through quantitative measurement and analysis, the system can also realize the judgment of the dominant microbial process (nitrification and / or denitrification, soil respiration) in the soil at a specific time; combined with further gas composition analysis, it is possible to clarify the nitrification and denitrification The contribution rate of nitrification to soil N2O emissions, to understand the impact of changes in environmental factors on N2O gas production and emissions, so as to accurately estimate and predict greenhouse gas emissions.

2.2 Collection of soil samples
Under natural conditions, a representative typical area is selected as the sampling plot; under experimental research conditions, a specific area is selected as the sampling plot according to the purpose of the study. According to the conditions of plot type, openness and flatness, soil homogeneity and other conditions, "plum blossom", "checkerboard", "S" and "grid method" can be selected for layout. For the same type of soil samples, take 3 to 7 undisturbed soils This is repeated. The time and frequency of sample collection are determined according to the research object and purpose. For specific operations and details, please refer to the relevant sections in Soil Physical and Chemical Analysis.
2.3 Measurement index
Real-time CO2 concentration and its variation, O2 real-time concentration and its variation, atmospheric pressure, soil temperature, temperature in the upper space of the cultivation room, total soil nitrification rate, soil denitrification rate, soil respiration rate.
2.4 Composition of measuring system
AZ-S0101 soil carbon and nitrogen conversion rate measurement system consists of soil sampling unit, soil carbon and nitrogen conversion rate measurement unit (including airtight measurement room, ZrO2 oxygen sensor, infrared CO2 sensor, air pressure sensor, temperature sensor, data transmission interface unit), constant temperature The water bath measurement unit and the environmental factor measurement unit (soil temperature, soil water content, soil pH, etc.) are composed together.
3 Data processing
3.1 Data record and result display
During the experiment, the AZ-S0101 soil carbon and nitrogen conversion rate measurement system automatically records and saves data through the software. At the end, the software automatically performs linear regression calculations to obtain the total nitrification rate, denitrification rate, and soil respiration rate (units are μgN / kg SDW / h) data, and displayed in the form of the following figure.
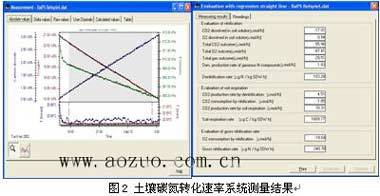
The software can also be adjusted into data files to correct parameters such as soil pH and soil water content that were not determined before the experiment and recalculate.
3.2 Data calculation
The system focuses on the three soil microbiological processes of soil respiration, nitrification, and denitrification in the soil, monitoring O2 consumption (â–³ O2), CO2 production (â–³ CO2), and total gas change (â–³ n).
Soil respiration process: CH2O + O2? CO2 + H2O
Heterotrophic nitrifying bacteria nitrification process: NH4 + + 2O2? NO3- + H2O + H +
Autotrophic nitrifying bacteria nitrification process: NH3 + 1.68O2 + 0.23CO2? 0.05C5H7O2N + 0.86H2O + 0.95HNO3
Denitrification process: 5CH2O + 4NO3- + 4H +? 5CO2 + 7H2O + 2NxOy
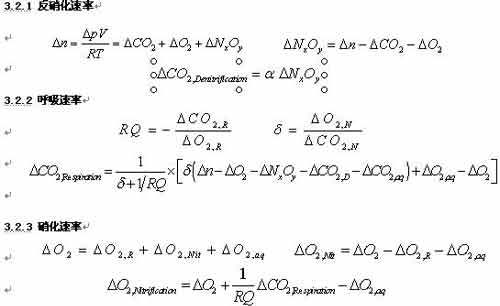
3.3 Model fitting
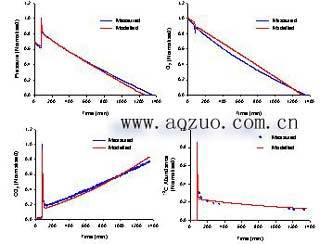
The system is based on certain theoretical assumptions and uses the measured data to derive the calculation results. Among them, some specific parameter values ​​need to be set, such as the ratio of N2 to N2O in NxOy, and the soil respiration moisture RQ. Fitting the experimental data with the theoretical model can realize the backstepping of specific parameters, thereby verifying the rationality of the set values.
4 Application case
4.1 Application of AZ-S0101 soil carbon and nitrogen conversion rate measurement system in the study of seasonal changes in nitrification and denitrification of alpine meadow soil
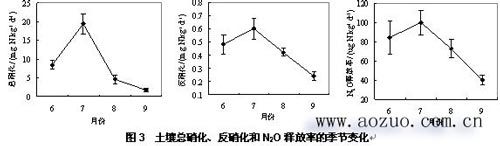
Figure 3 Seasonal changes of soil total nitrification, denitrification and N2O release rate
Relevant researchers at the Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences used the AZ-S0101 soil carbon and nitrogen conversion rate measurement system to determine the seasonal dynamics of nitrification and denitrification of alpine meadow soils in northwestern Sichuan. The results showed that: during the growing season of plants, the trends of soil total nitrification, denitrification and N2O release rate were consistent. Nitrogen material basis (NO3--N and NH4 + -N) is not the main factor affecting the nitrification and denitrification of the alpine meadow soil. Soil temperature and humidity are the main factors affecting the nitrification and denitrification of the alpine meadow soil.
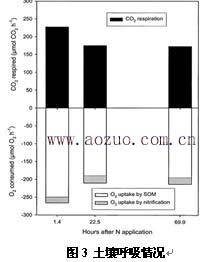
4.3 Application of AZ-S0101 soil carbon and nitrogen conversion rate measurement system in soil respiration research
Christoph Mu¨ller used the BaPS and 15N dilution methods to determine the nitrification rate of the same soil sample in the original grassland. Using the AZ-S0101 soil carbon and nitrogen conversion rate measurement system, the oxygen involved in nitrification and the oxygen in soil organic matter respiration can be calculated separately. The most sensitive parameter calculated by the BaPS technique is the amount of respiration of organic matter. The effects of nitrification and denitrification were corrected, and different breaths were marked differently. The test results show that: in the soil cultivation test, 6-10% of oxygen is consumed during the nitrification process; using the AZ-S0101 soil carbon and nitrogen conversion rate measurement system to measure the same soil sample under different soil temperature and moisture conditions, The results show that up to 49% of the oxygen is nitrified during the nitrification process; the respiration of soil organic matter measured by the combined technique of BaPS–15N is very close to the previous research data.
Short Body Soup Barrel,Stainless Steel Soup Container,Stainless Steel Stainless Steel Pot,Stainless Steel Large Pot
Jiangmen Vanky Stainless Steel Products Co., Ltd. , https://www.vankystar.com