h. Check. Screen inspection is the final process of the entire plate making work and it is also an extremely important process. The small defects exposed after the development can be corrected by revision. If a major defect occurs, it must be re-plated. In the quality inspection of the screen, at least the following issues should be emphasized.
Is the exposure time correct? In addition to measuring the degree of film hardening with a density ladder, you can also see how fine the reproduction of the bottom plate is on the screen, whether the lines are complete, whether the edges are clear, the jaggedness is serious, and so on.
The mesh is completely transparent. Check the quality of the screen printing plate, including whether the picture and text are all developed, whether there are burrs, broken lines, broken pens, and dead holes on the screen, if the above conditions are found, promptly adopt various methods to remedy the situation. Consider remaking plates to ensure print quality.
Only very transparent mesh can make screen printing ink pass through smoothly. If it is found that the perforated mesh on the screen plate is still sealed by the film, it should be developed again. If there is still no effect, it should be re-plated.
Examine the adaptability of various photosensitive materials. Different photo-resist films have different adaptability. For printing materials using organic solvents as diluents, solvent-resistant photographic films should be used; for water-based coatings, water-resistant photographic films should be used, and the two should not be confused. This inspection work should be combined with the use of manuals, and understanding of the substrate can only be correctly grasped.
Check for omentum, blisters, and unsealed mesh on the four sides near the frame. Bubbles and trachoma should be promptly remedied. The four-sided screen is screened to avoid ink leakage during printing. Use adhesive tape to attach the screen to the adhesive part of the frame.
Check the printing orientation markings for compliance with printing requirements.
i. Direct plate method failure and reasons.
The loss of photosensitive film during development cannot be made into a plate.
a) Underexposure.
b) The sensitizer dose is insufficient or invalid, and the sensitivity is reduced.
The full-page image produces a slight ash.
a) The work place in the coating and drying process of the photosensitive liquid is too bright.
b) Insufficient positive film density.
c) The exposure time is too long.
d) Overheating when the photosensitive liquid is applied and dried.
e) Insufficient exposure time and insufficient development.
The subtle part of the image is not developed.
a) The exposure time is too long.
b) The positive and negative sides are reversed and the positive film is poorly attached to the photosensitive film.
c) Insufficient screen treatment.
d) The photosensitive film is too thick and the type of the photoresist is not properly selected or the photoresist is ineffective.
The coated screen plate contains a lot of air bubbles.
a) Insufficient screen degreasing treatment.
b) The screen is not clean before coating the photosensitive adhesive.
c) The temperature difference between the screen drying and the photoresist during the coating process is large.
d) The storage temperature of the emulsion is too high.
e) The photoresist and the coating layer are too thin.
f) The coating speed is not uniform.
There are too many pin holes in the layout.
a) Dust is the main cause.
b) Sometimes it is caused by the bubbling of the photosensitive liquid itself.
c) When using a coating squeegee, the coating squeegee moves too quickly and it is prone to blistering to produce pinholes.
d) Addition of excess photosensitizer can also produce pinholes.
e) The coated surface is very easy to get dusty. Therefore, it is necessary to keep the workplace clean. For example, the printing glass surface, the positive printing film surface, and the photosensitive liquid coating surface must be kept completely clean.
f) A small amount of octanol can be added as a defoamer to the photosensitive liquid.
Visible pores appear after screen printing plate development.
a) Has high-temperature drying been performed after development (this should be noted).
b) The sensitizer with a long shelf life is used.
c) Whether dust has fallen into the emulsion.
d) Whether the sensitizer and the emulsion are mixed with sufficient stirring to be used after bubbles disappear.
e) Know if the exposure time is appropriate.
Photographic text resolution is not high after printing.
a) Whether the development is sufficient, and whether it is flushed with clean water after development.
b) The screen for secondary use has been cleaned before use.
c) Whether the screen is in a horizontal position and dry.
d) Whether or not to choose a high resolution photo resist.
j. Multi-color version positioning. Multi-color printing screens and printing plates must be prepared for the printed sleeves, so that the registration marks on the color separation sheets fall on the same positions of the screens. Otherwise, it will cause troubles for the upper edition, change edition and overprint of the printing, and even cause the discarded version. Here are two ways to locate:
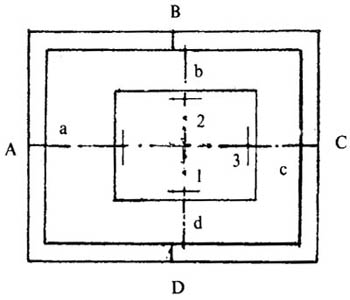
Figure 2-117 Positioning of separation printing
Measuring register method. In advance, the centerline coordinates are engraved on the four borders of each frame. After the screen has been set up, the centerline of the frame is gently extended to a certain extent with a pencil; the coordinates of the centerline on the negative and the screen are set. The centerline coordinate coincidence registration, as shown in Figure 2-117, 1, 3 and a, c or according to the provisions of the printing position, in the screen version of the actual coordinate line, and then register with the positive film, as shown 2, 4 and b, d. After registration, stick it with tape to expose it.
Pin, hole register method. Pin hole registration (Figure 2-118a) can improve the efficiency and accuracy of the fitting and reduce labor intensity. It is also a standardized and systematic register operation. That is, the manuscript and the color separation positive film are pin-holed, and the positive film and the screen are also fitted with a pin hole. The operation method of the latter is as follows:

Figure 2-118 Version Chart with Pins
First make a transparent layout (Figure 2-118c). The size of the frame and the center line are drawn on the plate. There are three holes above and on the left side of the plate. Three pins (Fig. 1-118b) are inserted in the holes and they are firmly bonded with tape for the screen to use.
Then use a screw or epoxy glue to fix the pin sheet on the plate.
In color separation printing, the matching plate is placed in the printing frame, and the positive plate with the positioning holes is placed on the positioning pins of the matching plate. The screen plate is positioned by three pins. This ensures that each screen on the screen Consistent with the bit.
Another method is shown in Figure 2-119. Attach the positioning pin to the glass of the printer, and attach the clip to the frame. During the printing, the positive film and the screen plate are both placed on the positioning pin.