There are many kinds of board warpage, first try the following methods for classification:
1. Cardboard warpage of the basic type a) parallel to the machine (MD or end-to-end);
b) Cardboard warpage in the direction perpendicular to the machine (CD or edge-to-edge);
c) Warp of composite (a certain form of twist) cardboard.
2, the basic shape a) downward (normal) cardboard warping;
b) upward (reverse) board warping;
c) Warp of composite (S-type) cardboard.
3, observation time a) directly from the corrugated board production line;
b) Seen after a few hours or more.
Figure 1 combines the basic types and shapes of cardboard warping in a series of squares:
a) The warpage of the cardboard parallel to the machine is arranged in the vertical or Y-axis direction;
b) The warpage of the board in the direction perpendicular to the machine is arranged horizontally or in the X-axis direction;
c) Warp of composite cardboard produced by combining two warpages.
The basic types and shapes of the nine kinds of board warping described in the box are not actually “symmetrical†as shown in the figure. It is actually difficult to bend the corrugated board into a symmetrical shape in the machine parallel direction and the machine vertical direction at the same time. Cardboard is usually flipped on one side or the other, resulting in asymmetrical, warped warping.
The real cause of cardboard warping
In a broad sense, the warpage of the board is caused by the non-uniform variation in the size of the components of the corrugated board, especially the change of the core paper. Cardboard warpage usually occurs after the corrugated tip and the backing paper are firmly bonded and no relative movement (slipping) between them occurs.
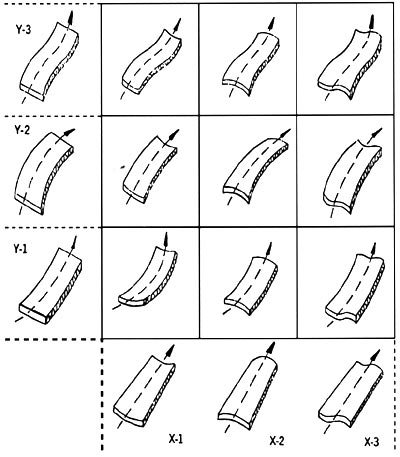
Figure 1: Six categories of nine basic shapes for cardboard warping
1, machine direction cardboard warping
Machine-direction (MD) board warpage is caused by uneven movement of the upper and lower papers in the rolling direction of the machine due to the cyclical changes in unbalance and unbalance of various forces in the rolling direction of the machine (end-to-end S Cardboard warpage). The main force here is the web tension.
If the tension of the upper sheet is higher than the tension of the lower sheet, the end-to-end upturned cardboard warps (Y-1 square in Fig. 1). This kind of warpage occurs because the upper sheet has a higher degree of stretch than the lower sheet after the sheet is bonded. Therefore, the elasticity of the cardboard back is greater and the tension is released when the cardboard is cut. Conversely, if the tension of the lower backing paper is higher than the tension of the top sheet, the end-to-end undercut board warps (Y-2 square in Fig. 1).
As a result, end-to-end S-board warpage occurs if large amounts of tension occur on either side of the paperboard or on both sides of the paperboard.
2, corrugated cardboard warpage
Cardboard warpage in corrugated direction (CD) is mainly caused by non-uniform changes in the corrugation direction of the upper and lower sheets caused by the original unbalanced forces in the corrugated parallel direction. The main force here is due to the change in moisture content, the so-called “wet-up†characteristic of the base paper, which causes the shrinkage force and expansion force. This wetting property is far greater in the direction of the corrugation than in the machine direction, which also shows that the most serious problem we encountered was the warpage of the cardboard in the direction of the corrugations, and at the same time it showed how troublesome the wet and mottled lines were in the base paper.
Effect of Variation of the Moisture Content of Base Paper on Warpage of Corrugated Cardboard
Roughly speaking, a 1% change in the moisture content of the base paper will change the size of the board in the corrugated direction by 0.06% to 0.10%. As the board passes through the corrugated board production line, the change in moisture content can reach 15% to 20%, which may cause a relative change in board size of 0.9% to 2.0%. On an 80-inch (2.03 m) wide paperboard, this value is 0.72 inches to 1.6 inches (18 mm to 41 mm). This large size change has a great effect on the warpage of the cardboard. Therefore, controlling the moisture content of the base paper is crucial for the production of flat cardboard.
The change in temperature also causes a change in the size of the cardboard. However, its effect is relatively small for cardboard warpage. It is difficult to treat the temperature factor in isolation because changes in temperature often accompany or actually cause changes in the moisture content of the base paper. Therefore, it is credible to explain the cause of cardboard warpage in the direction of the corrugations by the changes and differences in the moisture content occurring during the manufacture of the cardboard.
Of particular note is the state of moisture content that occurs on the bond of the backing paper and the corrugated tip of the hot plate, which often occurs when the paste is bonded. The force that causes a change in the state of moisture content refers to the mechanical forces that are generated when the formed cardboard is restricted to a straight state between the upper belt and the hot plate. At the bond of the base paper and the corrugated tip, the moisture content of the single-sided paper is much higher than that of the double-sided bottom paper. Not only is the additional moisture content of the single-sided paper glued to pass through the single-sided machine and the overpass When it is completely removed, and the moisture content produced when the double-sided liner is bonded is also transmitted to the single-sided paper.

Figure 2: Condition of the moisture content of the molded paperboard at the bonding point
Because the double-sided backing paper can only be firmly bonded after most of the moisture content on the paste has been removed, careful temperature measurement shows that the surface of the top paper between the corrugated tips will be dry and sticky. From these two factors, it is generally expected that the bond of the double-sided base paper will be very dry.
When the cardboard leaves the machine, the moisture content of single-sided paper (upper-layer paper) is much higher than double-sided paper (double-sided liner). When the moisture content of these two types of tissues is consistent with the moisture content of the surrounding air, the upper layer of paper will release moisture and shrink, while the double-sided bottom paper will expand due to the absorption of moisture. These two forces will cause the cardboard to rise. (Forward) Cardboard warpage. Unfinished
This article is provided by Minli Machinery Engineering Co., Ltd.