1 Introduction
In color printing, CMYK4 color overlay printing is often used, and Qing and Yang 1999-02-12 receive red, yellow, and black pigments to produce color images. These four basic colors combine to present up to eight colors: red, green, blue, cyan, magenta, yellow, black, and white, and a color image contains far more than eight colors. Units with large-scale professional color publishing systems, such as color production centers or printing plants, use color image processors to color-code color images into 4-color grayscale images, and then raster images (RIP) to grayscale images. Using the size of the dot or dot density to reflect the continuous tone of the grayscale image, the final four-color printing is performed using a laser photocopying mechanism to produce four-color films. Most color image makers do not have professional image processing technology and expensive image processing equipment. They hope that the color image can be arranged through a interface software to achieve color image color separation, color correction and hanging network, and finally to the printing plant Plate printing, which is more economical in terms of system cost and flexibility. Color image separation and hooking are the main problems to be solved by this interface software.
2 color image separation technology
2.1 RGB color model and CMYK color model
To facilitate computer processing of colors, color models are often used to describe colors. There are many kinds of color models that describe colors. Among them, RGB color models are used for CRT color image display, and CMYK color models are used for color image printing.
·RGB color model
The RGB color model is also referred to as additive color model. The color comes from the superposition of different luminances of the three basic colors of red, green, and blue, so the additive color model is called. It is mainly used to describe the color of light emitting devices, such as displays, televisions, scanners and other devices. In the model, the red, green, and blue light colors are measured with 256 tone values. Each channel assigns a numerical value to describe its tone, and the combination of the three light values ​​of different tone values ​​creates a rich color pattern. Color space, such as: each channel tone value is 255, the combination can produce white light; red channel bit 255, the rest is 0, you can simulate the effect of pure red; each channel tone value is 0, then Pixels are black; pixels have different shades of grey when the gradation values ​​are the same for each channel.
·CMYK color model
The CMYK color model is also called a subtractive color model. The colors come from the three primary colors of cyan, magenta, and yellow. These three primary colors absorb some colors from the white light on the illuminated paper, thus changing the light wave to produce colors, that is, subtracting some from white light. Color produces color, so it is called subtractive color model. It is mainly applied to the occasion where the physical substances such as printing ink and toner produce color, such as the field of color printing. In the model, each pixel value of a color image is measured by the percentage of cyan, magenta, yellow, and black inks, the percentage of inks of light-color pixels is lower, and the percentage of inks of deep-color pixels is higher, and the case of no ink is white. .
In the CMY color mode, theoretically, white paper reflects 100% of incident light, and mixing CMY3 100% colors absorbs all light and produces black. In the actual printing, the paper always absorbs some light, and the cyan, magenta, and yellow primary inks inevitably contain some impurities. Therefore, the black formed by 100% of the 3 primary color combinations tends to appear turbid gray, and the blackness is not enough. To compensate for this defect, A black pigment, K-color, was added to the print and this was called the CMYK model.
· Relationship between RGB and CMYK color models
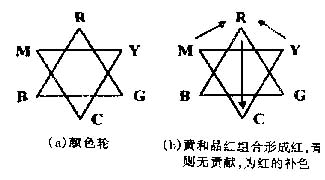
The RGB and CMYK color models look very different, and they are essentially complementary. The color wheel can be used to describe this relationship, as shown in Figure 1. The colors on the color wheel are arranged with each other, and any color can be combined with the colors in the adjacent opposite color models. The color in the inverse color model that does not contribute to the formation of a color is called the complementary color of this color. It can be known from the color wheel that cyan, pink, and yellow are complementary colors of red, green, and blue, respectively. This relationship between the RGB color model and the CMYK color model is the basis for the conversion between the two models and lays a theoretical foundation for the color image color separation technology.
2.2 Separation technology often
The color images used are all images of the RGB color model. Color separation is the decomposition of color images into cyan, magenta, yellow and black color grayscale maps, so color separation technology is the first to convert various colors in color images from RGB color model to CMYK color model, and then color The image is stored as a grayscale image of four colors of cyan, magenta, yellow, and black. It can be seen that the key to color separation technology is the color space conversion technology.
Based on the above relationship between the RGB color model and the CMYK color model, we obtain the content ratios of C, M, Y, and K required when a certain color on the original image is produced by the CMYK ink combination. The two models have the following relationships: C=F-R; M=F-G; Y=F-B where F is the full-color value. For any color C, M, Y, if its component is not 0, there is a gray component whose size is min(C,M,Y). In the actual printing, black pigment is added in order to make up for the defect that black formed by subtractive primary colors is not black enough. At the same time, the use of black pigment can also save a large number of color pigments, directly with the black pigment to form a different gray level, instead of subtractive 3 primary color combination. In this way, after the introduction of the black pigment, there will be redundant components of blue, pink and yellow. The content of cyan, pink and yellow in the actual printing must be reduced by the content of the portion replaced by the black pigment. Therefore, the conversion relationship between the RGB color model and the CMYK color model can be illustrated in Figure 2:

Some explanations are needed for this conversion relationship: (1) The gamut of the RGB color model has a larger color gamut than the CMYK color model. Some color combinations of the RGB color space cannot be represented by the colors of the CMYK color space. When the conversion is performed, these colors will be cut off and only converted to similar CMYK colors as much as possible, so there is a problem of one-time conversion. (2) The conversion formula of Figure 2 is only implemented under ideal conditions. In practical applications, due to factors such as the characteristics and composition of pigments, the effect of printing the image according to the above formula is difficult to meet the requirements of the application, so the conversion factor of the color space must be corrected to ensure the output of the color image. quality.